0.初めに
初めに
C# から利用できるソケット通信のクラスには、次の2つがあります。この章では、この2つのクラスをより使いやすくするための工夫に関して記述します。
- TcpListener
サーバ側のソケット通信用クラス - TcpClient
クライアント側のソケット通信用クラス
TcpListener のインスタンスを生成して、起動させます。外部からの接続要求をひたすら待ち続けるのがサーバ側のソケット通信クラスの役割です。
この状態を接続待ち状態といいます。
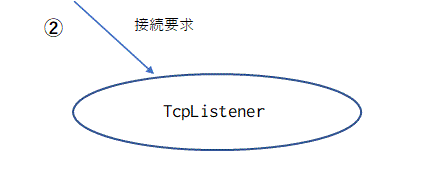
接続待ち状態の TcpListener に外部から接続要求が届きます。
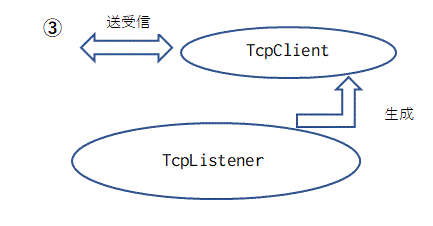
TcpListener クラスは接続要求に対応するための専用の TcpClient を生成します。TcpClient のインスタンスは、接続要求先の相手と送受信する作業を担当します。
この TcpClient のインスタンスは、
TcpListener のスレッドとは異なる専用のスレッド上で動作します。
TcpListener クラスが、外部接続先との送受信作業を直接行うことがないようにしましょう。
外部との送受信作業は専用の TcpClient に任せましたので、TcpListener クラスは受信待ち状態に戻ることができます。
こうすることにより、複数の接続要求にすばやく対応することが可能になります。
ここまでがソケット通信の基本です。以降では、さらに使いやすくする工夫について考えましょう。
1.解決方法
以下の章では、2つの中心的なクラスと、その動作をサポートするための2つの補助クラスを取り入れます。
この章のサンプルは、別の話題に関連して取り上げようと思います。それまでのお楽しみに。
クラス
TcpServer クラス
TcpListener クラスを機能拡張したクラスが TcpServer クラスになります。
そのプログラムを次に示します。
1 public class TcpServer
2 {
3 private const string localhost = "127.0.0.1";
4 public static Func<DoubleStatusObject, TcpClient, TcpServerSideClient> MakeClient
5 {
6 get; set;
7 }
8 public Int32 Port
9 {
10 get; set;
11 }
12 public string Address
13 {
14 get; set;
15 }
16 protected StatusObject status;
17 public TcpServer() : this(localhost) { }
18 public TcpServer(string address)
19 {
20 this.status = new StatusObject();
21 Port = -1;
22 Address = address;
23 MakeClient = null;
24 }
25 public void ToRunning()
26 {
27 status.ToRunning();
27 }
28 public void ToStop()
29 {
30 status.ToStop();
31 }
32 public void Run()
33 {
34 if (Port <= 0 || string.IsNullOrEmpty(Address) || MakeClient == null)
35 throw new InvalidOperationException();
36 TcpListener server = null;
37 try
38 {
39 IPAddress localAddr = IPAddress.Parse(Address);
40 server = new TcpListener(localAddr, Port);
41 server.Start();
42 while (!status.IsStop())
43 {
44 if (!server.Pending())
45 {
46 Task.Delay(500);
47 continue;
48 }
49 TcpClient tcpClient = server.AcceptTcpClient();
50 TcpServerSideClient client = MakeClient(new DoubleStatusObject(status), tcpClient);
51 Task task = new Task(() => client.Run());
52 task.Start();
53 }
54 }
55 catch (Exception)
56 {
57 throw;
58 }
59 finally
60 {
61 if (server != null)
62 server.Stop();
63 }
64 }
65 }
| 3行目 | 接続待ちするデフォルトのアドレス先です.標準ではローカルホストになります |
| 4~7行目 | 接続先と送受信処理を担当するオブジェクトを生成するためのメソッドです. この処理を別建ての static メソッドとすることで、任意の送受信用オブジェクトを生成できるようにしています |
| 8~11行目 | 接続待ちするポート番号用のプロパティです |
| 12~15行目 | 接続待ちするアドレス用のプロパティです |
| 16行目 | TcpServer の状態を表す StatusObject です.後述する補助クラスの1つです |
| 17行目 | デフォルトのコンストラクタです.デフォルトではローカルホストからの接続待ちになります |
| 18~24行目 | 接続待ちするアドレスを指定したコンストラクタです |
| 25~27行目 | 状態を開始にします.実際の処理を開始するには、 Run() メソッドを呼び出します |
| 28~31行目 | 状態を終了にします.実際の処理終了は、Run() メソッドの中で行います |
| 32~65行目 | クラスの中心となる処理です |
| 34~35行目 | 処理開始の条件がそろっていない場合、例外を投げます |
| 36行目 | 標準クラスの TcpListener オブジェクト用変数です |
| 39行目 | 接続待ちするアドレスを準備します |
| 40~41行目 | 標準クラスの TcpListener オブジェクトを生成して、接続待ち処理を開始します |
| 42~53行目 | 状態が終了となるまで、 TcpServer の処理を継続します |
| 49~50行目 | TcpServerSideClient オブジェクトを生成します.後述します |
| 51~52行目 | 新しいスレッド上で、TcpServerSideClient のオブジェクトの処理を開始します |
| 55~63行目 | エラー処理と終了時の処理です |
TcpServerSideClient クラス
TcpClient クラスを機能拡張したクラスが TcpServerSideClient クラスになります。
そのプログラムを次に示します。
1 public abstract class TcpServerSideClient
2 {
3 protected DoubleStatusObject status;
4 protected System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient Client
5 {
6 get; private set;
7 }
8 public Encoding Encoding
9 {
10 get; set;
11 }
12 public Action<NetworkStream> Action
13 {
14 get; set;
15 }
16 public TcpServerSideClient(DoubleStatusObject status, TcpClient client)
17 {
18 Client = client;
19 this.status = status;
20 Encoding = Encoding.UTF8;
21 Action = null;
22 }
23 public virtual void Run()
24 {
25 if (Client == null || Action == null)
26 return;
27 status.ToRunning();
28 try
29 {
30 NetworkStream stream = Client.GetStream();
31 while (!status.IsStop())
32 {
33 Action(stream);
34 }
35 }
36 catch (Exception)
37 {
38 throw;
39 }
40 finally
41 {
42 if (Client != null)
43 Client.Close();
44 }
45 }
46 protected virtual string Read(NetworkStream stream)
47 {
48 int size = 0;
49 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
50 MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream();
51 do
52 {
53 size = stream.Read(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
54 if (size <= 0)
55 break;
56 ms.Write(bytes, 0, size);
57 } while (stream.DataAvailable || bytes[size - 1] != '\n');
58 string msg = Encoding.GetString(ms.GetBuffer(), 0, (int)ms.Length);
59 ms.Close();
60 return size == 0 ? null : msg;
61 }
62 protected virtual void Write(NetworkStream stream, string msg)
63 {
64 byte[] bytes = Encoding.GetBytes(msg);
65 stream.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
66 }
67 protected virtual void WriteLine(NetworkStream stream, string msg)
68 {
69 Write(stream, msg + "\r\n");
70 }
/// <summary>
/// 文字列の最後にある任意個の改行コード("\r","\n", "\r\n")を取り除いた文字列を返す
/// 文字列の途中にある改行コードはそのままにする
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msg">改行コードを取り除きたい文字列</param>
/// <returns>改行コードを取り除いた文字列</returns>
71 public static string RemoveLine(string msg)
72 {
73 if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(msg))
74 return msg;
75 int cnt = 0;
76 for (int i = msg.Length - 1; i >= 0; --i)
77 {
78 if (msg[i] == '\r' || msg[i] == '\n')
79 ++cnt;
80 else
81 break;
82 }
83 return cnt == 0 ? msg :
84 cnt == msg.Length ? string.Empty :
85 msg.Substring(0, msg.Length - cnt);
86 }
87 }
| 3行目 | オブジェクトの状態を表します.後述します |
| 4~7行目 | 対応する標準のクラス TcpClient 用のプロパティです |
| 8~11行目 | 送受信データのエンコーディング用のプロパティです |
| 12~15行目 | 処理の本体に対応した Action ラムダ式です |
| 16~22行目 | コンストラクタです.TcpServer クラスから呼び出されます |
| 23~45行目 | 処理の本体です.状態が停止となるまで、Action ラムダ式を繰り返し呼び出します |
| 46~61行目 | 受信した文字列を返します.受信エラーの場合に、空文字列を返します |
| 62~66行目 | 文字列を送信します |
| 67~70行目 | 改行文字を付けた文字列を送信します |
| 71~86行目 | 受信処理で使用するサポート用メソッドです |
StatusObject クラス
TcpServer クラスの状態を表すクラスです。内容は単純ですので、説明は不要でしょう。
public class StatusObject
{
public enum Status { Running, Stop, Suspend };
protected volatile Status status = Status.Stop;
public StatusObject()
{
status = Status.Stop;
}
public virtual void ToRunning()
{
status = Status.Running;
}
public virtual bool IsRunning()
{
return status == Status.Running;
}
public virtual void ToStop(Object owner = null)
{
status = Status.Stop;
}
public virtual bool IsStop()
{
return status == Status.Stop;
}
public virtual void ToSuspend()
{
status = Status.Suspend;
}
public virtual bool IsSuspend()
{
return status == Status.Suspend;
}
}
DoubleStatusObject クラス
TcpServerSideClient クラスの状態を表すクラスです。こちらは、StatusObject クラスより複雑になっています。TcpServerSideClient は自分自身の状態を持つだけでなく、起動元の TcpServer オブジェクトの状態にも影響されるからです。
TcpServer オブジェクトが処理を終了する場合には、自身の状態にかかわらず終了しなければなりません。そのため、起動元の TcpServer オブジェクトの状態変数 StatusObject オブジェクトをコンストラクタで受け取るようになっています。
さらに、自身の状態は自由に操作できる必要がありますが、起動元の TcpServer の状態は参照だけが可能になるようにする必要もあります。
このことが分かれば、ソースの理解は難しくないと思います。
public class DoubleStatusObject : StatusObject
{
protected StatusObject parent;
public DoubleStatusObject(StatusObject parent) : base()
{
this.parent = parent;
}
public override bool IsRunning()
{
return parent != null && parent.IsRunning() && base.IsRunning();
}
public override bool IsStop()
{
return (parent != null && parent.IsStop()) || base.IsStop();
}
public override bool IsSuspend()
{
return (parent != null && parent.IsSuspend()) || (parent.IsRunning() && base.IsSuspend());
}
}